

- Energy gap of P-N junction diode: To determine the energy gap of a semiconductor diode
- Solar Cell: To study the V-I Characteristics of solar cell
- Light emitting diode: Plot V-I and P-I characteristics of light emitting diode
- Stewart – Gee’s experiment: Determination of magnetic field along the axis of a current carrying coil
- Hall effect: To determine Hall co-efficient of a given semiconductor
- Photoelectric effect: To determine work function of a given material
- LASER: To study the characteristics of LASER sources
- Optical fibre: To determine the bending losses of Optical fibres
- LCR Circuit: To determine the Quality factor of LCR Circuit
- R-C Circuit: To determine the time constant of R-C circuit
Energy gap of P-N junction diode: To determine the energy gap of a semiconductor diode
Object:To determine the Energy Band Gap in a Semiconductor by using a Junction Diode.
Required apparatus: Semiconductor diode kit, thermometer (0-110oC)
Theory:
A semi-conductor doped or intrinsic always possesses an energy gap between its conduction and valence bands. For conduction of electricity, a certain amount of energy is to be given to the electron, so that it goes from the valence band to the conduction band. This energy so needed is the measure of the energy gap \Delta E between the top and bottom of valence and conduction bands respectively. When a P-N junction is reverse biased as shown figure1. the current through the junction is due to minority carriers i.e. due to electrons in P section and holes in N section. The concentration of these carriers depends upon the energy gap \Delta E.
For small range of temperature relation we can put as,
log Is = Constant – 5.036 \Delta E [103/T ]
Obviously therefore, if a graph is plotted between log Is and 103/T, a straight line would be obtained.
Where the slope of this line = 5.036 \Delta E
Here \Delta E is in electron volts.
Procedure:
- Plug the mains lead to the nearest mains socket carrying 230V 10% at 50 Hz A.C.
- Insert the thermometer and the diode in the holes of the oven (The hole near to the meter is for diode OA- 79).
- Plug the two leads to the diode in the socket, Red plug in Red socket and Black plug in Black socket.
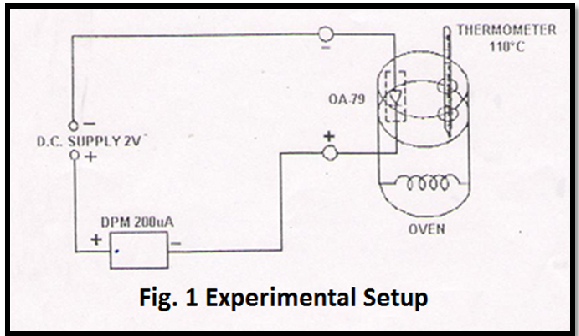
- Make the connection as per fig.
- Now put the power ON/OFF Switch to 'ON' position and see that the jewel light is glowing.
- Put the 'OVEN' switch 'ON' position and allow the oven temperature T increases up to 90oC.
- Note: When the temperature reaches 95oC Switch off the oven enabling the temperature to rise further and become stable 90oC
- When the temperature becomes stable start taking readings of current and temperature.
- The current reading should be taken in steps of 5ºC temperature. The readings should be taken during the fall of temperature from 80oC downwards.
Tabulate your readings in the form shown below:
Temperature in0 C
(absolute)
Reverse saturation Current in µA Is
Temperature T in 0 K
103/T
Log10Is
- Plot a graph between the readings of 103/T on x-axis. The graph should come as a straight line cutting both the x-axis and y-axis.
- Now determine slope of the line.
- After determining the slope the line calculate the Band Gap as follows:-
= .....................eV.
Determination of Slope through Least Square Fit Method:
|
xi=103/T |
yi=log10Is |
xiyi |
xi2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Slope and Percentage Error:-
% ERROR = \frac{(Standard\:\:\:Value\sim Observed\:\:\:Value\times 100)}{Standard\:\:\:Value}
Precautions:-
- The maximum temperature should not exceed 95oC
- Bulb of the thermometer should be inserted well in the oven,
- Silicon diodes should not be used with the set up as in that case the temperature needed is 125oC and the oven thermometer provided will not stand to this temperature.
Diagram:-
Q1 :
Q.1: What is diode?
Ans: The diode consists of two electrodes one is cathode and another is anode. The cathode emits electrons and the anode will attracts the emitted electrons when it is supplied by positive potential.
Q2 :
Q.2: What is energy band gap?
Ans: The gap between the bottom of conduction band and the top of valence band is called Energy gap. To move the electrons from the valence band to conduction band the supplied external voltage must be equal to energy band gap.
Q3 :
Q.3: What is valence band?
Ans: The range of energy which is possessed by valence electrons is known as valence band. Here the electrons which are situated at outer most orbits are called valence electrons. The valence band consists of valence electrons which are having highest energy.
Q4 :
Q.4: What do you mean by conduction band?
Ans: The range of energies possessed by conducting electrons is known as conduction band. The conduction electrons are responsible for the conduction of current in a conducting material. So, these electrons are called as conduction electrons.
Q5 :
Q.5: Classify the solid materials on the basis of energy gap.
Ans: Based on the energy gap the solid materials are classified into 3 types they are: conductors, insulators and semi conductors.
Q6 :
Q.6: Define conductors, insulators and Semi conductors.
Ans: Conductors: Those substances whose atoms have their outermost orbits incomplete are known as conductors (e.g. Cu, Ag, Au etc.). In conductors, valence and conduction bands are found overlapped into each other i.e. the energy gap is zero.
Insulators: Those substances which have large energy gap between their valence and conduction band, are called insulators (e.g. diamond, wood etc.).
Semi conductors: Those substances which have conductivity and resistivity properties in between conductors and insulators are called semi conductors (e.g. Si, Ge). Energy gap of these semiconductors lies between 0.5 to 1.1eV (Foe Ge it is 0.5 – 0.7eV).
Q7 :
Q.7: How many types of semi conductors are there?
Ans: Two types of semi conductors are there (i) Intrinsic or pure semi conductors and
(ii) Extrinsic or impure semi conductors.
Q8 :
Q.8: Define intrinsic and extrinsic semi conductor?
Ans: Intrinsic semi conductor: A pure semiconductor is known as intrinsic semi conductor. In these semi conductors, if the temperature increases then the conductivity is also increases. At higher temperatures due to collisions some electrons absorb energy and raises to conduction band then in their places in valence band holes are created. In intrinsic semiconductor number of holes is equal to number of electrons.
Extrinsic semi conductor: A pure semiconductor after doping is called extrinsic or impure semi conductor. Trivalent and penta-valent impurities are added to form P-type and N-type semiconductors respectively.
Q9 :
Q.9: What do you mean by Fermi energy level?
Ans: The level upto which all the energy states are filled by electrons is known as Fermi level. The average energy of charge carriers is calculated by Fermi energy level. In pure semi conductors Fermi energy level is at the centre of the valence and conduction bands. In extrinsic/impure P-type (N-type) semiconductor Fermi energy level is near to the valence (conduction) band.
Q10 :
Q.10: Define Doping and Dopant?
Ans: The process of adding impurities to a pure semi conductor is called doping
The material added as impurity is called as Dopant.
Q11 :
Q.11: What are P-type and N-type semi conductors?
Ans: If we add trivalent impurities such as Aluminum to a pure semi conductor then the material is called P-type semi conductor. If a pentavalent impurity such as Arsenic is added to a pure semi conductor then the material is called N-type semi conductor
Q12 :
Q.12: Why P-type (N-type) semi conductor is called Acceptor (Donor)?
Ans: In P-type material 3 electrons of trivalent atom makes covalent bonds with Semiconductors such as Si or Ge and there is a need of one more electron to make the system stable because Si or Ge has 4 electrons in their outermost orbits. For this reason P-type material is also known as Acceptor.
On the other hand, in case of N-type of material 4 electrons of pentavalent atom makes covalent bonds with Semiconductors such as Si or Ge which have 4 electrons in their outermost orbits and hence there is one free or excess electron remains present in the structure. For this reason N-type material is also known as Donor.
Q13 :
Q.13: What is P-N junction diode?
Ans: If P-type and N-type semi conductors are combined to each other then the resultant structure is called P-N junction diode. This means if trivalent impurity is doped to one end of the pure semi conductor and pentavalent impurity to other end, a P-N junction diode can be formed.
Q14 :
Q.14: What do you mean by Forward Biasing?
Ans: When a battery’s positive terminal is connected to P-type material and battery’s negative terminal is connected to N-type material of a P-N junction diode, then this mode of operation is said to be in forward biasing. Here the holes of P are repelled by the positive terminal of the battery and electrons of N are repelled by the negative terminal of the battery and hence both holes and electrons moves towards the junction. As the applied voltage becomes large enough to destroy the depletion barrier diode starts conducting. This Forward Biasing is also called as Low resistance connection. In this mode of biasing the current flow is mainly due to majority charge carriers.
Q15 :
Q.15: What do you mean by Reverse Biasing?
Ans: When a battery’s positive terminal is connected to N-type material and battery’s negative terminal is connected to P-type material of a P-N junction diode, then this mode of operation is said to be in forward biasing. Here the holes of P are attracted by the negative polarity of the battery and electrons of N are attracted by the positive polarity of the battery and hence both holes and electrons move away from the junction and then this increases the width of depletion layer. This reverse Biasing is also called as High resistance connection. In this bias the current is mainly due to minority charge carriers. In this mode, very small current flows across the junction.

0 Doubts's