

Determination of total hardness of water by complexometric method using EDTA
Determination of total hardness of water by complexometric method using EDTA
Aim: To estimate the amount of total hardness present in the given sample of water by EDTA titration method.
Apparatus required: 50 ml Burette, 20 ml Pipette, 250 ml Conical flask, 100 ml Beaker, 250 ml beaker, Glass funnel.
Reagents: EDTA solution, Standard CaCO3 solution, Eriochrome Black–T indicator, Buffer solution.
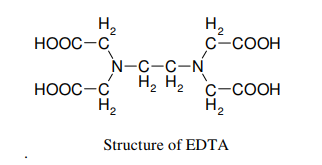
Theory: EDTA (Ethylenediamine tetra acetic acid) forms colorless stable complexes with Ca2+ and Mg2+ ions present in water at pH = 9-10. To maintain the pH of the solution at 9-10, buffer solution (NH4Cl + NH4OH) is used. Eriochrome Black-T (E.B.T) is used as an indicator.
The sample of hard water must be treated with buffer solution and EBT indicator which forms unstable, wine-red colored complex s with Ca2+ and Mg2+ present in water.
Procedure :
1 .Standardization of EDTA
(i)Pipette out 20 ml of standard hard water into a conical flask.
(ii) Add 5 ml of buffer solution and few drops of Eriochrome Black-T. The indicator, which is originally blue color would acquire a wine-red color.
(iii) Titrate with EDTA solution taken in the burette, till the wine red color changes to blue which is the end point. Let the burette reading of EDTA be V2 ml.
2.Determination of Total hardness
Repeat the above titration method for sample hard water instead of standard hard water. Let the burette reading of EDTA be V3 ml.
3.Determination of Permanent hardness
Take 100 ml of sample hard water in 250 ml beaker. Boil it to remove temporary hardness to about half of this volume and cool to room temperature. Filter through filter paper to remove insoluble CaCO3 and MgCO3. Make up the volume to the original 100 ml by adding distilled water. Now pipette out 20 ml of this solution into a clean conical flask. Then repeat the process of titration steps as mentioned above. Let the burette reading of EDTA be V4 ml.
Observations
1.Standardization of EDTA
| S.No | Vol.of Hard water taken (ml) | Burette Reading |
Vol.of EDTA Consumed (V2 ml) |
|
| Initial | Final | |||
| 1. | ||||
| 2. | ||||
| 3. | ||||
2.Determination of Total hardness
| S.No | Vol.of Hard water taken (ml) | Burette Reading | Vol.of EDTA Consumed (V3 ml) | |
| Initial | Final | |||
| 1. | ||||
| 2. | ||||
| 3. | ||||
3.Determination of Permanent hardness
| S.No | Vol.of Hard water taken (ml) | Burette Reading | Vol.of EDTA Consumed (V4 ml) |
|
| Initial | Final | |||
| 1. | ||||
| 2. | ||||
| 3. | ||||
Calculations
1.Standardization of EDTA
M1V1 = M2V2
Where, M1 = Molarity of standard hard water
V1 = Volume of standard hard water in conical flask
M2 = Molarity of EDTA
V2 = Volume of EDTA consumed (burette reading)
2.Determination of Total hardness
M2V2 = M3V3
Where, M3 = Total hardness of sample water
V1 = Volume of sample hard water in conical flask
3.Determination of Permanent hardness
M2V2 = M4V4
Where, M4= Permanent hardness of sample water
V4 = Volume of sample hard water in conical flask
Note: Multiply M3 and M4 with 105 to covert hardness into parts per million (ppm).
4.Determination of Temporary hardness
Temporary hardness = Total hardness – Permanent hardness
Result: The hardness of the given water sample has been found to be as follows:
Total hardness = ----------------------------- ppm
Permanent hardness = ----------------------------- ppm
Temporary hardness = ----------------------------- ppm

0 Doubts's