- Chemical equation
- Question And Answers
- Chemical equation
- Law of conservation of mass
- Laws of constant proportion
- Dalton’s atomic theory
- Atoms and molecules
- Symbols of elements
- Atomicity
- Valency
- What is an Ion ?
- Atomic mass
- Molecules of compounds
- Molecular mass , Formula unit mass
- Mole
- Molar mass
- Types of Chemical Reactions
- Decompostion Reaction
- Displacement reaction
- Double displacement reaction
- Oxidation and Reduction
- Effects of oxidation reactions in daily life
- 7.Atoms, Molecules And Chemical Reactions
- Atoms, Molecules, and chemical reactions
- Classification of Elements
- Dobereiner’s law of Triads
- Limitations
- Mendeleeff’s Periodic Table
- Salient features and achievements of the Mendeleeff’s periodic table
- Limitations of Mendeleeff’s periodic table
- Modern Periodic Table
- Groups,
- Periods
- Metals and Non metals
- Atomic radius
- Periodic properties of the elements in the modern table
- Ionization Energy
- Electronegativity
- Metallic and Non-Metallic Properties
- Short answer Questions
- Question And Answers
- Synopsis
- Classification of elements - The Perodic Table
- Nutrition
- Mechanism of Photosynthesis
- Light independent reaction (Biosynthetic phase)
- Heterotrophic nutrition and nutrition in Human Beings
- Health aspects of the elementary canal
- Coordination in life processes
- Peristaltic Movement in Esophagus
- Taste connected with tongue and palate
- Villi
- Respiration -The energy Producing system
- Epiglottis and passage of air
- Gaseous Exchange
- Respiration versus combustion
- Transportation-The circulatory system
- The blood vessels and The cardiac cycle
- Blood pressure and Materials transport in the plants
- The wastage disposing system
- Mechanisms of urine formation
- Other Pathways Of Excretion
- Excretion release in substance of plants
- Short Answer Questions
- Long answer Questions
- Synopsis
- Reproduction - The generating system
- Reproduction in a placental mammal - Man
- Cell cycle
- Reproduction In Organisms
- Parthenogenesis
- Vegetative Propagation
- Male Reproductive System
- Female reproductive system
- STRUCTURE OF A SPERM
- Menstrual Cycle
- Extra Embryonic Membrane
- Sexual reproduction in flowering plants
- Synopsis
- Long Answer Questions
- Short Answer Questions
- Quizz
- Important Quiz Questions
- Introduction
- Lewis Electron Dot Symbols
- Ionic Compounds: Electrons Transferred
- Formation of Ionic Compounds
- The arrangement of ions in ionic compounds
- Covalent bond
- VSEPR theory
- Valence bond theory
-
Formation of O_2, N_2, CH_4Molecules
- Hybridisation
- Properties of ionic and covalent compounds
-
Formation of BF_3,NH_3, water molecule
- Synopsis
- Question And Answers
- Chemical Bonding
Reproduction - The generating system
Reproduction - The generating system
In plants and animals reproduction is necessary life process for continuation of life by the production of offsprings.
Organisms are capable of giving rise to offsprings by the process of reproduction. Some organisms may reproduce differently in different situations. For example, in favorable conditions paramoecium give rise to more of its kind from a single parent by simply spliting into two. This happens rapidly and several of them are formed. During unfavourable conditions two paramoecia come in contact exchange certain materials of their bodies and produce forms that are more to tolerant.
The time required to reproduce also varies from organism to organism. Even within the organism there could be certain environmental conditions that would make faster the process of reproduction
Asexual mode of reproduction
Modes of reproduction involving a single parent, without involving gametes. These are known as asexual modes of reproduction. Organisms can reproduce asexually in many ways. Some of them are given here.
Fission
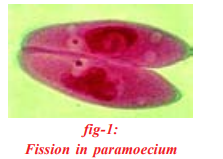
Single celled organisms, such as Paramoecium and bacteria, reproduce by splitting into two or more offsprings. This usually occurs in a symmetrical manner. They split into two by binary fission. When more cell are formed it is called multiple fission. This is often the only mode of reproduction in these organisms.
Budding
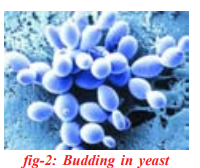
A growth on the body as a bud that grows to form nearly identical copy of parent. When the bud totally grows then it separates from the parent and survives independently.
Ex:Yeast.
Fragmentation

Some can grow from a separate piece of parent organism. This can be from any part of the body. This happens only in the simplest, such as some flatworms, moulds, lichens, Spirogyra etc. grow in this manner. These may also reproduce sexually. Fragmentation is a common mode of reproduction in algae, fungi and many land plants.
Parthenogenesis

Now a days we are able to develop seedless fruits like watermelon, grapes etc. This is a process of reproduction where there is a shift from sexual to asexual mode of reproduction.
This process also occurs in nature. An organism which reproduce sexually sometimes asexually. We have utilised this process of reproduction in growing organisms of our choice with more desirable characters. In this process generally the female gametes develops into zygote without fertilization
Regeneration
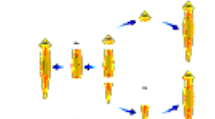
Many organisms have the ability to give rise to new individual organisms from their body parts. That is, if the
individual is somehow cut or broken up into many pieces, these pieces grow into separate individuals. This is similar to fragmentation.
Vegetative propagation

In higher plants vegetative propagation. may be natural or artificial.
Natural propagation
Leaves: In Bryophyllum small plants grow at the edge of leaves.
Stems: Aerial weak stems like runners and stolons, when they touch the ground, give off adventitious roots. When the connection with the parent plant is broken, the stem portion with the adventitious roots develops into an independent plant. Some examples for propagation by stem are from stolons, bulbs, corms, tuber, etc. Stolons - Vallisneria, strawberry, Bulbs - Alliumcepa or onion, Corms - Colacasia, tuber - potato,
Roots: Roots of Dahlia, radish, carrot etc., grow as new plants.

Artificial propagation
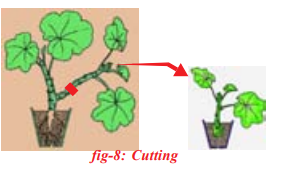
Cutting:
Some plants grow individually when a piece of a parent plant having bud is cut from the existing plant. The lower part of this cutting is buried in moist cell. After few days the cut parts having buds grow as an individual plant after developing roots. Ex: Rose
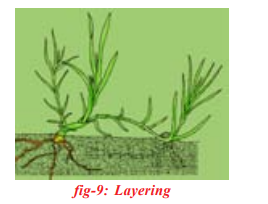
Layering:
A branch of the plant with at least one node is bent towards the ground and a part of it is covered with moist soil leaving the tip of the branch exposed above the ground. After some time, new roots develop from the part of the branch buried in the soil. The branch is then cut off from the parent plant, the part which has developed roots grows to become a new plant.
Ex:Nerium.
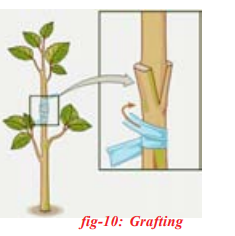
Grafting:
Two plants are joined together in such a way that two stems join and grow as a single plant. One which is attached to soil is called stock and the cut stem of another plant without roots is called scion. Both stock and scion are tied with help of a twine thread and covered by a polythene cover. Grafting is used to obtain a plant with desirable characters. This techqnique is very useful in propagating improved varieties of various flower and fruits
(ex: Mango, citrus, apple, rose).
If you have two varieties of fruit yielding trees in your garden. One tree has the character of giving big sized fruits but less in number. The taste of the fruit is pretty good. The other one produce more number of fruits but they are neither big in size nor tasty.
Spore formation:
Generally we may notice whitish threads and blackish powdery like substance on rotten fruits, bread slices and other food materials. When you touch it, the blackish powder sticks on your fingers. These are the reproductive spores produced by a fungi. Ex: Rhizopus.
Rhizopus produces hundreds of microscopic reproductive units called spores. When the spore case (also called sporangium) bursts, the spores spreads into air. These air-borne spores land on food or soil, under favourable conditions like damp and warm conditions, they germinate and produce new individuals. Most of the fungi like Rhizopus, Mucor etc.,
Bacteria and non-flowering plants such as ferns and mosses reproduce by the method of spore formation.
Sexual reproduction
As you havestudied earlier, sexual reproduction is a way of reproduction where fusion of gametes takes place, by a process called fertilisation. Fertilisation may occurs either outside the body of the mother (external fertilisation) or inside the mother’s body (internal fertilisation). As a matter of fact, the eggs of land animals are fertilised inside the body of the mother. The fertilized eggs start dividing and growing into the embryo.
External fertilisation is common in aquatic animals like most of the fishes and amphibians. The female lays a vast number of eggs in water and male release some millions of sperms on them in water. As the chance of
fertilisation is controlled by nature which occurs externally, hence it is inevitable to give rise to vast number of eggs and sperms (gamete).



0 Doubts's