- Nutrition food supply to System
- Mechanism of Photosynthesis
- Light independent reaction (Biosynthetic phase)
- Heterotrophic nutrition and nutrition in Human Beings
- Health aspects of the elementary canal
- Synopsis
- Long answer Questions
- Short Answer Questions
- Quiz Questions
- Important quiz questions
- Important quiz questions
- Reproduction - The generating system
- Reproduction in a placental mammal - Man
- Cell cycle
- Reproduction In Organisms
- Parthenogenesis
- Vegetative Propagation
- Male Reproductive System
- Female reproductive system
- STRUCTURE OF A SPERM
- Menstrual Cycle
- Extra Embryonic Membrane
- Sexual reproduction in flowering plants
- Synopsis
- Long Answer Questions
- Short Answer Questions
- Quizz
- Important Quiz Questions
Nutrition food supply to System
Nutrition food supply to System
- Food is needed by all living organisms mainly for growth and repair. Several organisms need food to maintain body temperature as well.
- A large variety of substances are taken as food from single cellular organisms like an amoeba to the complex multicellular organisms like the human body.
- Even within the human body the cells require a wide variety of substances as food.
- The mode of acquiring food also varies from cell to cell and organism to organism.
Types of Nutrition :
There are mainly three types of nutrition
- Autotrophic Nutrition
- Heterotrophic Nutrition
1. Autotrophic Nutrition :
The term ‘autotroph’ is derived from two Greek words – auto means ‘self’ and 'troph' means ‘nutrition’, in autotrophic nutrition an organism makes its own food from simple raw materials.
This nutrition can be of two types.
- Photoautotrophs
- Chemoautotrophs
Photoautotrophs :
- Green plants synthesize food through the process of photosynthesis, using simple raw materials like water and CO2 in the presence of sunlight.
- Chloroplast is the site of photosynthesis.
- Chlorophyll is the photosynthetic pigment which trap solar energy and is present in the chlorophyll.
$$ 6CO_{2} + 12H_{2}O + Light $$ $$ energy \rightarrow C_{6}H_{12}O_{6} + 6O_{2} + 6H_{2}O $$
- Since autotrophic plants are able to produce food for others therefore they are also know as producers.
- Because the autotrophic nutrition is the characteristic of plants, therefore, it is also called halophytic nutrition.
Chemoautotrophs :
- Some non–green bacteria like Sulphur bacteria use chemical energy to manufacture their food.
- This energy is derived from chemical reactions occurring in the bacteria.
- This process is called chemosynthesis.
- Chemosynthetic bacteria do not require light as the source of energy.
$$ 2H_{2}S + O_{2} \rightarrow 2H_{2}O + S + 126 K.Cal $$
$$ 2S + 2H_{2} + O_{2} \rightarrow 2H_{2}SO_{4} + 141.8K.Cal $$
2. Heterotrophic Nutrition :
- The word ‘heterotroph’ is derived from the Greek words – hetero (different) and troph (nutrition or food).
- Heterotrophic organisms obtain large organic substances (as food) from other organisms, unlike autotrophs, which manufacture their own food.
- As heterotrophs depend on other organisms for their food, therefore, they are called consumers.
- All animals, fungi and no green plants come under this category.
Nutrition In Plants: Photosynthesis
- The process by which green plants make their own food from CO2 and H2O by using sunlight energy in the presence of chlorophyll is called Photosynthesis.
- Oxygen gas is released during photosynthesis.
- The process of photosynthesis can be represented as:
| $$\begin{matrix} 6CO_2\rightarrow 6C+6O\\ 12H_2O\rightarrow12H \end{matrix}$$ |
$$\begin{matrix} +6O\\ +12H \end{matrix}$$ |
$$+12O$$ |
| $$6CO_2+12H_2O\rightarrow C_6H_{12}O_6$$ | $$+6H_2O$$ | $$+6O_2$$ |
- The green plants convert sunlight energy into chemical energy by making glucose (foods).
- The extra glucose formed in the above process is changed into starch which gets stored in leaves of plants.
- The oxygen comes from the water.
- The synthesis of carbohydrate food materials mainly through the process of photosynthesis occurs in the green cells of the plant.
- Therefore, the food from these cells is transported to the non-green part through the phloem.
- This process is called translocation.
Conditions for Photosynthesis :
- Sunlight
- Chlorophyll
- Carbon dioxide
- Water
Sunlight :
Chlorophyll is a green pigment mainly present in green plants which trap sunlight and converts them into chemical energy during photosynthesis. The plant utilizes only visible light which consists of seven colors, out of them green color light has minimum absorption. It gets reflected which makes plants look green in color.
Chlorophyll :
It is a green pigment and mainly present in the green leaves of the plants. There are many different types of chlorophylls, namely a, b, c, d, e, and bacterio-chlorophyll. Out of these, chlorophyll ‘a’ and chlorophyll ‘b’ are the most abundant and most common forms of chlorophyll.
Carbon dioxide :
It is a gas present in the air. Green plants take CO2 which get absorbed by leaves through stomata.
Water :
It is required by plants for photosynthesis and is absorbed by the roots of plants from the soil through the process of osmosis. Water gets transported upward through the xylem to the leaves.
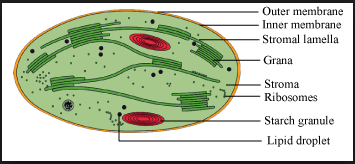
T.S OF CHLOROPLAST
Illustration 1:
Name of two pigments other than chlorophyll which absorbs sunlight.
Solution:
Carotenoids, Fucoxanthin
Exercise :
Name the green pigment present in the leaves of plants?
Ans: Chlorophyll
At the compensation point, the rate of two opposite processes taking place simultaneously in a plant becomes equal. Name these two processes?
Ans: Photosynthesis and Respiration
How do aquatic plants get carbon dioxide for photosynthesis?
Ans: They absorb CO2 soluble in water by the process of diffusion.



0 Doubts's