- Introduction
- Exercise 2.1 - part 1
- Exercise Problems-2.1 - Part 2
- Exercise 2.2
- Exercise 2.3- part 1
- Exercise 2.3 - part 2
- Algebraic Identities
- Example Problems-2.4
- Exercise 2.4 - part 1
- Exercise Problems 2.4 - part 2
- Exercise Problems 2.4 - part 3
- Exercise 2.5 - Part 1
- Exercise Problems 2.5 - part 2
- Introduction
- Surface Area and Volume of a Cube
- Surface Area and volume of a Cuboid
- Surface Area and Volume of a Right Circular Cylinder
- Surface Area and Volume of a Hollow Right Circular Cylinder
- Surface Area and Volume of a Right Circular Cone
- Surface Area and Volume of a Sphere
- Surface Area and Volume of a Hemisphere
- Exercise 10.1
Introduction (Basic terms and Definitions)
Introduction
Basic Terms and Definitions
1. Point :
A Point is that which has no component. It is represented by a dot.
2. Line :
When we join two distinct points then we get a line. A line has no endpoints it can be extended infinitely.
3. Line Segment :
It is the part of the line which has two endpoints.
4. Ray :
Ray is also a part of the line which has only one endpoint and has no end on the other side.
5. Collinear and Non-collinear points :
Points lie on the same line are known as collinear points and the points that don't lie on the same line are known as Non-Collinear Points.

collinear points Non-Collinear Points
Angles :
When two rays begin from the same endpoint then they form an Angle. The two rays are the arms of the angle and the endpoint is the vertex of the angle.
Types of Angles :
| Angle | Notation | Image |
| Acute | An angle that is between 0° and 90°. | 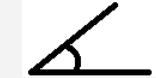 |
| Right | An angle that is exactly equal to 90°. | 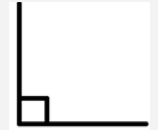 |
| Obtuse | An angle is between 90° and 180°. |  |
| Reflex | An angle which is between 180° and 360° |  |
| Straight | An angle that is exactly equal to 180°. | |
| Complete | An angle that is exactly equal to 360°. | 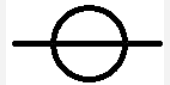 |
Complementary and Supplementary Angles :
Complementary Angles are those which have the sum of two angles as 90°.
Supplementary Angles are those which have the sum of two angles as 180°.
The relation between two Angles :
| Angles | Relation | Image |
| Adjacent Angles | If two angles have the same vertex and their one of the arm is common then these are called adjacent angles. | 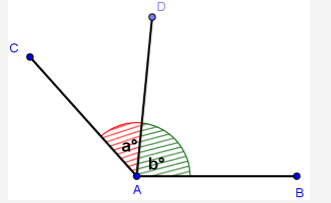 |
| Linear pair of Angles | If two angles have the same vertex and one common arm but the arms which are not common are making a line then these are called the linear pair of angles. | 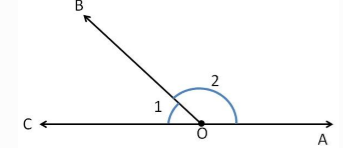 |
| Vertically opposite Angles | If two lines intersect each other at a point then the opposite angles are vertically opposite angles. | 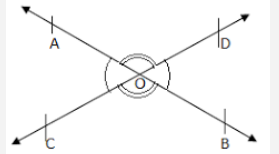 |



0 Doubts's